Sarcopenia Prevention With Eccentric Exercise
Treatment GuidelinesAccording to a recent article in New York Times, “few practicing physicians alert their older patients to this condition." Learn how you can intervene to protect your elderly clients from age-related muscle loss.
If you work with elderly patients, you’ve probably seen your fair share of age-related muscle loss, known as sarcopenia. It can cause loss of function and independence in severe cases.
According to a recent article in New York Times, “few practicing physicians alert their older patients to this condition and tell them how to slow or reverse what is otherwise an inevitable decline that can seriously impair their physical and emotional well-being and ability to carry out the tasks of daily life.” 1
As therapists, we can help prevent and even reverse sarcopenia with exercise. By taking advantage of one specific muscle group, you can help elderly patients retain function and independence.
Sarcopenia
Most of us accept sarcopenia as an inevitable part of aging. As elderly patients lose muscle mass, we can expect some loss of strength and function. By age 80, most people lose half of their skeletal muscle2.Unfortunately, this muscle loss decreases functional abilities, and increases the chances of a fall.
In fall prevention, much of the danger arises with the loss of fast twitch / type 2 muscle fibers. Loss of this fast twitch muscle fiber is associated with sarcopenia. In other cases, skeletal muscle can become infiltrated with fibrous and adipose tissue3. This infiltration reduces the quality of the muscle fibers, making them weaker and less powerful.
These changes in the skeletal muscle lead to a reduction in the quality of muscle fibers making muscles weaker and less powerful. Eventually, an individual can become increasingly sedentary which leads to further comorbidities or they may experience premature mortality4.
Fast Twitch / Type 2 Muscle
As therapists, we can delay sarcopenia and preserve patients’ quality of life. One of the most vital muscle groups to preventing sarcopenia is fast twitch / type 2. Especially for fall prevention, strengthening fast twitch muscles is essential.
Resistance Exercise for Muscle Loss
We engage fast twitch muscle fibers in most daily activities. From athletic training to injury prevention, we rely on them for function and safety. However, usually among the first to degenerate as we age.
Thankfully, we can build those muscle fibers with resistance exercise. Studies show that resistance exercise can reverse age-related muscle loss. Elderly patients performing resistance exercise regain function as their fast twitch muscles grow larger and stronger5. This outcome can prevent injuries for your elderly patients as well.
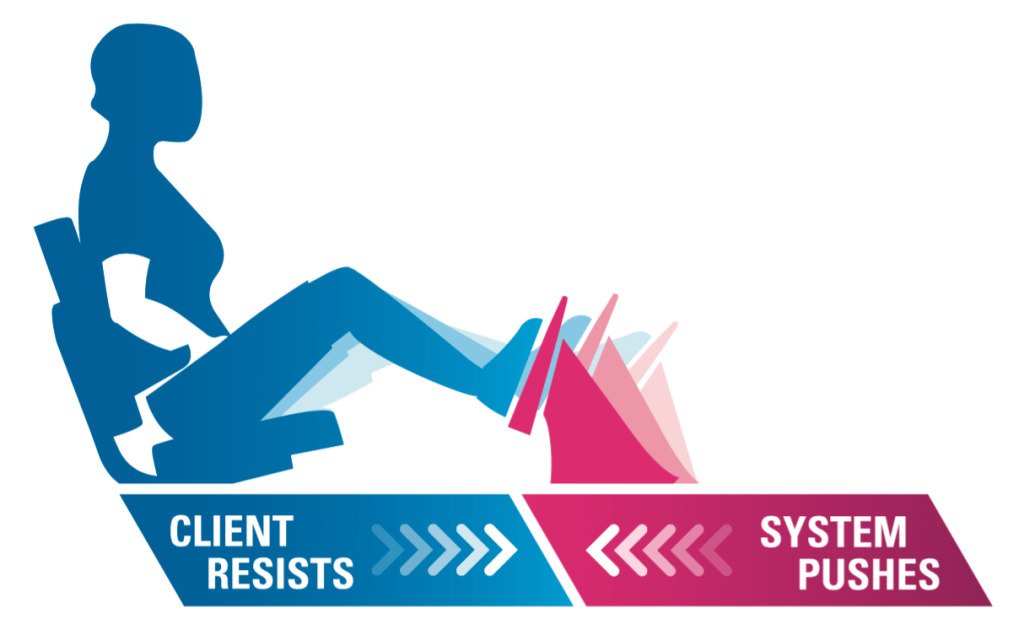
The best way to target fast twitch muscle is with eccentric exercise. Eccentric exercise uses negative resistance, so the muscle can tolerate higher loading.
For example, patients using the BTE Eccentron resist the moving pedals at their own force capacity. The motion is like walking down stairs or lowering a weight. It’s great for elderly patients, as it requires low energy input, and yields high force output.
In fact, eccentric exercise has played a starring role after complex surgeries, recovering from injuries, and living with debilitating conditions.
Clinical Trial Using Eccentric Exercise for Sarcopenia
For example, one study examined the strength of elderly patients. One group performed traditional exercises while the other exclusively did eccentric exercise. The eccentrics group had about 20% more strength gains, and improved in functional tests6. These results reduced the patients’ fall risk and improved their quality of life.
A Natural Decline, but not the End of the Road
As we age, we naturally lose some muscle mass. But sarcopenia doesn’t have to mean loss of function. With early intervention, we can combat sarcopenia. Therapists can have a profound influence on slowing the negative consequences of aging.
Especially for patients at risk for falling, it is imperative to work with them on both short- and long-term goals in fall prevention. With preventive exercise and strengthening, you can prevent a fall from leading to a more serious health concern. The right exercise plan can vastly improve your patients’ quality of life.
Jeffrey Johnson, MA, ATC
Clinical Specialist
BTE
References
- Walston JD. Sarcopenia in older adults. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2012;24(6):623–627
- Lexell J. Human aging, muscle mass, and fiber type composition. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1995;50:11–16
- Hanson E, Srivatsan S, Agrawal S, et al. Effects of strength training on physical function: influence of power, strength, and body composition. J Strength Cond Res. 2009;23(9):2627–2637
- Ferrucci L, de Cabo FR, Knuth ND, Studenski S. Of Greek heroes, wiggling worms, mighty mice, and old body builders. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67:13–16.
- LaStayo P, Woolf J, Lewek M, Mackler Lynn, Reich, T, Lindstedt S. Eccentric Muscle Contractions: Their Contribution to Injury, Prevention, Rehabilitation, and Sport. JOSPT. 2003: 33 (10): 557-571.
- Snijders T, Verdijk LB. The impact of sarcopenia and exercise training on skeletal muscle satellite cells. Ageing. 2009 Oct: 8 (4): 328-338.
- LaStayo P, et al. The Positive effects of negative work in frail elderly population. Journal of Gerontology: Medical Sciences. 2003, Vol 58A, (5). P419-424.